What to Do With Early Literacy Assessments? Easy Framework To Make The Right Decisions
Reading assessments are a big part of evidence-based literacy instruction. While foundational reading skills like phonics and phonological awareness often dominate discussions, the assessment of these skills do not get as much airtime.
Especially in the early years, assessing students’ reading development does not automatically equip educators to translate those results into effective instructional decisions.
As a matter of fact, schools often find it difficult to effectively use assessment and accurately interpret their results to enhance reading outcomes.
Even with high-quality instruction, the absence of robust assessment planning can deepen inequities in access to effective reading instruction for students who need them most.
School-wide reading assessments are now more prevalent and a required component of multi-tiered systems of supports (MTSS). It’s high time that early literacy teams receive clear guidance about their usage.
This article guides early literacy teams in selecting the right assessments to meet learning goals and maximizing the impact of their assessments.
In order to do this, it proposes the framework: Information. Action. Deliberation.
Information.

What Questions Are Early Literacy Teams Trying to Answer?
Interpreting assessment results without understanding their purpose can lead to misguided actions for students.
Therefore, it’s crucial for literacy teams to first identify the key questions they need answered.
To effectively use current tools or consider adopting new tools, teams must analyze the information needs thoroughly.
Research on various assessment tools touch on the following information needs.
Information Needs
- How many students at each grade are proficient in reading?
- Which students need additional support to meet end-of-year expectations?
- What specific reading skills do students need additional instruction in?
- What specific supplemental instruction is required for students?
- Are students making progress toward meeting research-based expectations?
- Are students receiving appropriate interventions at the various tiers, making progress towards their learning goals?
Action

What Decisions will Answering These Questions Allow Early Literacy Teams To Take?
If an information needs analysis proves challenging, then the literacy team can think about the decisions that they are looking to make with the information.
In other words, if formulating questions proves difficult, focus on how the answers to those questions benefit the early literacy team and their students.
This approach strengthens the information needs analysis, helping to choose the right assessment tools for specific purposes.
To demonstrate, the previous question examples have now been paired with their corresponding actions:
How many students at each grade are proficient in reading?
Answer helps to: Understand progress towards strategic objectives, evaluate current curriculum and classroom resources.
Which students need additional support to meet end-of-year expectations?
Answer helps to: Allocate resources and time for those students currently performing below standard.
What specific reading skills do students need additional instruction in?
Answer helps to: Identify targeted tier 2 and tier 3 classroom instruction, to ensure children are receiving the support they need, when they need it.
What specific supplemental instruction is required for students?
Answer helps to: Provide teachers with evidence-based instructional practices that help provide personalized instruction for every student.
Are students making progress toward meeting research-based expectations?
Answer helps to: Ensure students are on track with learning the foundational reading skills and support teachers to continue or intensify their existing instructional practices.
Are students receiving appropriate interventions at the various tiers, making progress towards their learning goals?
Answer helps to: Identify the need to continue, intensify, fade or modify their existing intervention approach.
_________________________________________________________________________
Note how certain answers help to decide binary actions, that is whether to do something or not, while others help to get clarity over making individual or group decisions for students.
This is expected.
Actions vary, some target school-wide strategies, while others focus on specific classroom and/or student-level interventions.
These distinctions must be considered when deciding how to use early literacy assessments.
Deliberation.

Provide Assessment Types for The Decision To Be Made.
Performing steps one and two, that is, determining the right questions to gather information and the actions based on those answers are crucial for selecting the appropriate assessment tool.
This is because these questions and answers are internal, directly addressing the school’s specific needs and goals.
Every assessment tool in the market has its own purpose. They are external, unless developed organically by the school.
By understanding what is required first, an early literacy team can easily pick the assessment tool/s that best suits their purpose.
Deliberation is the final step.
The right early literacy assessment strategy and tools must be carefully deliberated on, so they provide the precise information needed to drive effective actions.
How Can You Do This?
-
Understand What the Different Categories of Assessments Are.
How many types of assessments do you need to meet all your objectives? Is one sufficient, or do you need multiple? Sprig Learning explores this topic in another blog.
Recapping the major assessment categories’ description from 11 Key Questions for Selecting The Right Early Literacy Assessment(s) for Your School.
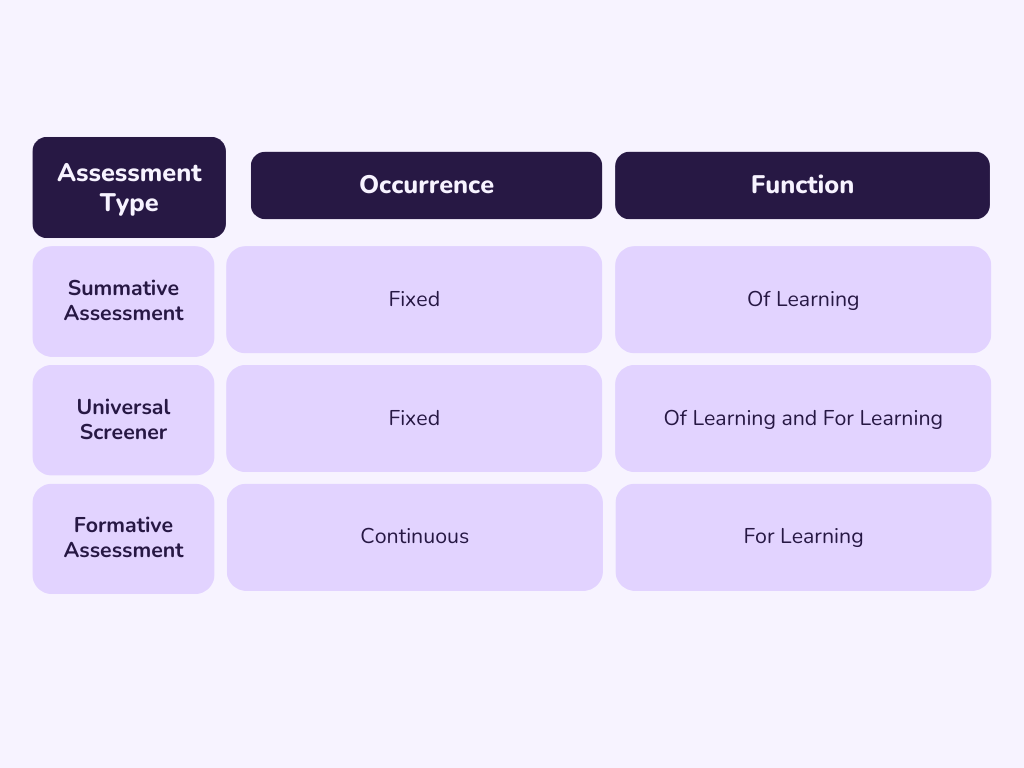
Universal Screening Assessments- Identifies students at risk. Helps to evaluate core instruction.
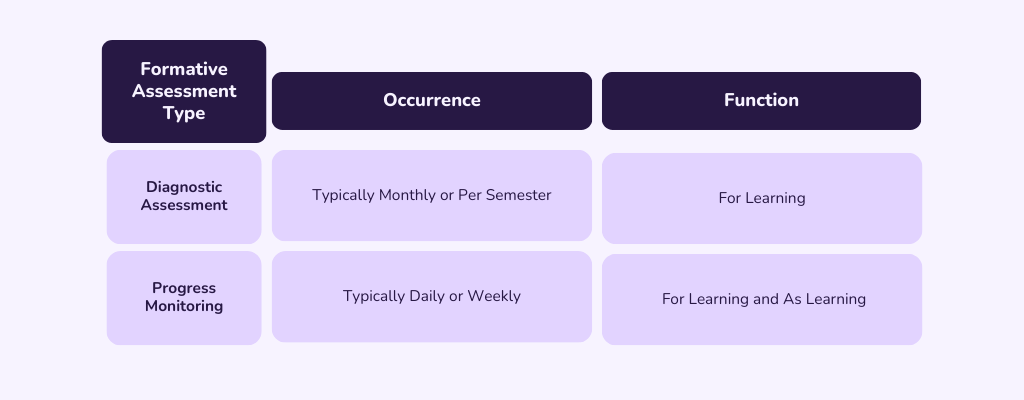
Diagnostic Assessments- Identifies strengths and areas of need. Helps to plan and implement instruction and intervention.
Progress Monitoring Assessments- Identifies if students are responding. Evaluates the extent to which students are on track to meet research-based targets.
-
Understand Which Data From Selected Assessment/s Will Provide Most Value.
Vendors provide multiple scores in their assessment solutions, so it’s important to pick the right one that will be suited to the purpose.
For measuring growth, scaled scores should be used instead of grade-level scores.
The grade-level metrics only reflect differences in text complexity, not the actual growth in students’ reading abilities. They are helpful for making classroom assessments.
For individual students, schools should focus on interpreting the scaled score specific to each assessment.
-
Understand How to Set Decision Rules
For setting decision rules, there are two major components of determining if an intervention is required or if the current intervention is working. It can be at any tier of MTSS.
- Set a predetermined goal.
- Establish criteria for evaluating whether the student/group/class is on track to meet the goal.
Decision rules must be set for every type of assessment.
Let’s take progress monitoring as an example, as its high frequency of data collection provides a faster data-based decision cycle.
The Oregon Department of Education recommends the four point decision rule and the slope analysis.
The former takes the four most recent data points to a pre-set research-backed goal line. If they are all below the goal line, the intervention is adjusted due to insufficient growth. If they are all above the goal line, the intervention is faded or a new line is set. If they are both above and below the line, the current intervention is continued.
There is also a slope-analysis where a linear trend is fit into existing data points to characterize the trend in their overall actual growth. The steepness of the student’s growth trend is compared to the slope of the goal line.
When setting decision rules, consider what’s needed to close a gap and realistically evaluate how much progress an intervention can achieve within a set timeframe. Goals for progress monitoring should account for both these factors.
-
Understand The Needs of the End User.
Administrators use screening scores for scheduling and resource decisions, like identifying students needing extra support. These scores offer a general view of reading development but lack the detailed information teachers need for lesson planning.
Since a single assessment suite generates various scores, it’s important to determine which scores are most useful for each group.
Aligning on these needs can enhance collaboration and support better student literacy outcomes.
Information. Action. Deliberation.

Apply It Today To Perfect Early Literacy Assessments Across All Tiers
The Reading League comments, if 85% of students are not proficient in foundational skills with a Tier 1 curriculum, the issue likely lies with the program or its implementation, not the students.
But this is overwhelmingly the case for almost every school across the continent!
This is why many leading literacy organizations recommend in their curriculum evaluation guidelines that assessment data be used to differentiate instruction across a Multi-Tiered System of Supports based on student progress.
Core instruction and its assessment is just as important as any supplementary measures taken in any of the other tiers in MTSS.
So when deciding what to do with early literacy assessments, the framework outlined in this article of information, action and deliberation helps to gain an overall understanding of the needs of every student, and every end-user.
It resolves tension between the type of reading assessment scores that administrators and teachers find useful in their roles.
It helps to methodologically think about all objectives that are in stake, and the information areas that are needed in order to meet them.
Sprig Reading 3.0 Has Launched!

Effective in whole group, small group, and individual intervention settings, Sprig Reading supports differentiated instruction to ensure every child masters the foundational skills needed to read at grade-level.