The Science of Reading (SoR) is picking up steam in schools in North America. It’s a methodology consisting of evidence-based literacy practices that have proven to work in increasing literacy achievement for early learners.
The SoR is informed by decades of research into what is most effective at teaching children to read. The knowledge of what makes a successful reader is taken from multiple disciplines and is an expanding body of research.
At present, there is enough evidence to support a shift towards teaching practices that are aligned to SoR.
Sprig Learning wrote about the application of SoR in various stages of early literacy development. Indeed, SoR should be a part of every early literacy strategy.
In this article, we look at multiple aspects of SoR to derive lessons that can be applied in the classroom.
To do this, we rely on an assortment of 40 factual statements on SoR. They are grouped where appropriate, to offer valuable insights to educators, staff and leaders for improving reading instruction at schools.
Using these 40 insights and other important realizations gained through research and experience, Sprig is committed to bring SoR into the classroom this fall with the launch of Sprig Reading.
Improvement starts at a strategic level. Let’s see how SoR advises strategic reading instruction.
40 Insights to Inform Strategic Reading Instruction

1. The SoR must not ignore language, identity, culture and other contexts that are important to the early reading experience.
Recommendation
There is another side to SoR that probes deeper into the learning context of the young student. While offering direct, systematic and explicit instruction, it also understands the unique background and learning profile of each student. This can be done through holistic assessments.
2. Studies show that computer-assisted instruction is valuable in improving the phonological awareness of 6-year-old children.
Recommendation
Phonemic awareness is one of the major pillars of SoR, which in turn is a part of phonological awareness. It’s important to note that technology has the power to catapult the instruction of these concepts into another level of efficiency!
3. The simple view of reading equation (see image below) shows that reading comprehension is the product of decoding/recognition and oral language comprehension. It has been tested in over 100 studies and endorsed by many renowned reading experts.
Simple View of Reading
Decoding (D) x Language Comprehension (LC) = Reading Comprehension (RC)
4. The Scarborough Rope Model of Skilled Reading (see image below) states that word recognition (which includes phonological awareness, decoding and sight recognition) and language comprehension come together to form the fluent execution of skilled reading.
The Scarborough Rope Model of Skilled Reading
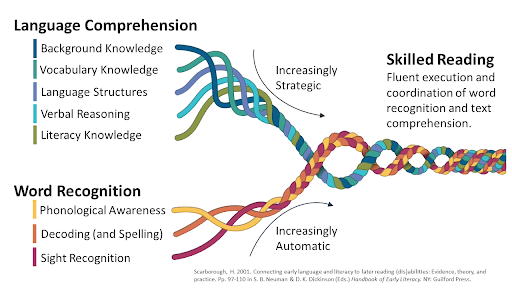
Recommendation From 3 & 4
The simple view of reading is one of the main models used when talking about SoR. Decoding is used in phonemic awareness and phonics, two of the main pillars of SoR. Oral language permeates in every pillar of SoR, but especially vocabulary and phonemic awareness.
Reading comprehension is the result of children recognizing letters and the sounds they make, and understanding the meaning of the words they form.
The Scarborough Rope Model of Skilled Reading also backs this notion of word recognition (of which decoding is a part of) and language comprehension (of which vocabulary is a part of) coming together to produce skilled readers.
So while the decoding bit is rather obvious to SoR, oral language is also important to integrate in lessons.
5. Research has identified poor phonological awareness as a major risk factor for dyslexia. Intensive phonological awareness instruction can be used as an intervention for readers with dyslexia.
6. Many readers struggle with reading fluency, which has been linked to poor ability in Rapid Automatized Naming (RAN). RAN is the ability to quickly name letters, symbols, words, or objects in a quick and automatic manner.
7. Relatively small difficulties encountered in the early months of learning how to read, such as problems with phonological processing or letter-to-sound matches, discourage students from practicing reading. For lack of practice, these early learners fail to grow their vocabularies, gain reading fluency, or acquire other background knowledge needed to comprehend texts.
Recommendation From 5-7
Along with phonological awareness (this includes phonemic awareness), RAN, and Shared Reading and Concepts of Print are extremely important in building fluency in the early stages of one’s reading journey. This is why these concepts are a part of the Joyful Literacy Framework, used by Sprig Reading.
Although not part of the original 5 pillars of SoR, RAN and Shared Reading and Concepts of Print have been deemed important enough to focus on separately, and should be a part of reading instruction.
8. There are over 40 research centers in the US dedicated to examining reading-related brain activity. Research in these centers have been ongoing for more than three decades.
9. 15-20 % of students are dyslexic. While dyslexia cannot be cured, intensive reading instruction can help improve the success rates of dyslexic students.
10. Learning to read requires the involvement of several brain functions. The visual cortex recognizes printed letters and words. It is located in the occipital lobe.
11. The auditory cortex builds oral word understanding. It is located in the temporal lobe.
12. The angular gyrus associates letters with sounds. It is located in the parietal lobe.
13. The inferior frontal gyrus produces speech and processes meaning. It is located in the frontal lobe.
14. 56% of variance in reading outcomes are due to the increase in volume of brain white matter between kindergarten and Grade 3. The quality of instruction during this time period impacts the building of the neural pathways.
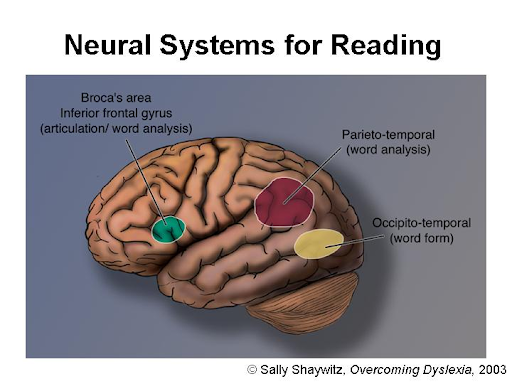
Recommendation From 8-14
Ultimately, learning how to read is partly a biological process. It has to do with functions in the brain.
Given the urgency and gravity of early language development, Sprig Learning always vouches for early literacy intervention, that is taking action, when the student is most conducive to learning concepts and building good habits.
15. There are certain leadership practices that significantly raise the percentage of students’ reading at grade level by Grade 2. Schools that have been successful in raising this number share 5 behaviors. They:
16. Make literacy priority number one.
17. Treat reading instruction time as sacred.
18. Empower teachers to own and lead interventions.
19. Monitor processes and data closely.
20. Share granular data with students.

Recommendation From 15-20
Leveraging SoR for strategic reading instruction is not a task for educators only. They must be adequately backed by school and district leaders.
When there is a system in place where educators are given the time to focus on literacy instruction, formative assessments and interventions, accountability is increased for all.
Teachers and administrators are aware of what is working, and the student also knows what areas they need to improve on. This information can also be shared with parents, who can be more actively involved.
21. 90- 95% of students have the cognitive capacity to read.
22. 30% of students are capable of reading regardless of instructional quality.
23. 50% of students are capable of learning how to read from explicit and direct instruction in foundational skills.
24. 15% of students will need additional time and support to meet their reading potential.
25. 5% of students have severe cognitive disabilities.
Recommendation From 21-25
While it’s true that there will always be a certain percentage of students who will continue to struggle to read because of cognitive impairments, the vast majority of students should be able to read with varied levels of support.
The biggest segment from this group of students is those who will need help using SoR in order to boost their literacy scores. By first implementing SoR in the classroom and following it up with tiered intervention support, the overwhelming majority of students (90-95%) can be helped. This is a far cry from the average of 35% of students who are currently reading at grade level at Grade 4 in the US.
26. A randomized controlled longitudinal study conducted by Vanderbilt University shows that preschool education improves reading outcomes, but the effects are not sustained beyond kindergarten.
27. 79% of the variance in high-school reading ability is explained by the intensity of foundational skills instruction in Grade 1.
28. There is a thing called the Grade 4 slump, where 20% of Proficient Grade 3 readers drop down to Basic by Grade 5. 55% of advanced readers in Grade 3, are no longer advanced readers in Grade 5. There have been 90 research studies which say that the absence of foundational phonics and phonemic awareness instruction in the early grades impairs students’ reading growth in the later grades.
29. Research from the University of Chicago has found that for 85-90% of struggling readers, intervention programs implemented before Grade 3 can increase reading skills to an average level. However, if the interventions come after Grade 3, then 75% of those students will continue to struggle with reading.

Recommendation From 26-29
High-quality early literacy instruction is extremely important to literacy growth, but it has to be consistently applied, beginning in preschool, and especially in kindergarten, Grade 1 and Grade 2. If not, then the early efforts are not sustained to achieve maximum reading potential.
Plans to improve kindergarten and primary school programs are as important as the need for high-quality preschools and early childhood programs.
Instruction early on in kindergarten and Grade 1 has to be intensive, in order to give kids their best shot at success in the later grades. It is absolutely crucial that any literacy interventions are applied before Grade 3. If these interventions are started at preschool, it’s important that they are not stopped after preschool.
30. The concept of spoken language was invented over 200,000 years ago, however the concept of written language was invented only 5,500 years ago.
31. 87% of words in the English Language are either fully or easily decodable.
32. Approximately 80% of elementary teachers do not adequately teach phonemic awareness to their students, if at all.
33. 95% of early elementary classrooms spend inadequate time providing direct instruction on all the English phonemes.
34. The National Reading Panel (NRP) established the 5 pillars of reading instruction in 2000. To meet the NRP recommendation of more phonics instruction, schools adopted balanced literacy. But in balanced literacy, phonics is taught only briefly.
35. In a study of 32 elementary schools in Rapides Parish School Board, the percentage of kindergarteners reading at grade level rose from 46% to 99% because of science-of-reading training, data summits, skills-based grouping and summer learning focused on literacy.
36. In a study of 16 elementary schools in The Bethlehem Area School District, the percentage of kindergarteners reading at or above the DIBELS benchmark composite score increased from 47% to 84% due to science-of-reading training, new curriculum, skills-based grouping and summer learning focused on literacy.
37. UP Academy Holland, which is a part of Boston Public Schools, shifted from balanced literacy to a high-quality English language arts curriculum that was built to support the Science of Reading. Ever since its implementation, they have noticed a decrease in behavioral issues in language blocks, greater confidence from students in responding to questions and reading, and more enthusiasm from both students and teachers!

Recommendation From 30-37
Reading language was a human invention and so it requires a specific methodology for teaching it. As long as that methodology is applied, as demonstrated in numerous case studies, the likelihood of increasing literacy scores rises.
Phonemic awareness and phonics have to be incorporated into lesson plans. It’s not the case currently in many schools where educators are underprepared. A good SoR should have adequate professional development support so educators can be quickly upskilled on how to teach phonemic awareness and phonics.
38. In a survey of Pre-K to 3 teachers, there were three types of challenges faced in literacy instruction. These were time, resources and materials, and diversity of student needs. There was not enough time to work individually with students. This included both struggling and accelerated learners. It was difficult to find reading materials in multiple languages, and appropriate leveled texts for older students who would not be embarrassed to read them. Regarding diversity of student needs, teachers found it difficult to manage striving readers, where they would get pulled out of class, but then miss out on other instruction in class.
39. The common causes for reading instructional failure include: inadequate or non-existent review and repetition cycle, lack of real reading and writing experiences, inappropriate reading materials to practice skills, loss of time due to transitions, and limited teacher knowledge of research-based phonic routines.
40. Multi-sensory approach to reading enhances phonics instruction. Manipulatives, gestures, and speaking and auditory cues improve early learners’ acquisition of phonics skills. Multi-sensory activities also provide the necessary scaffolding to beginning and struggling readers. They include visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile activities to enhance learning.
Recommendation From 38-40
These last three statements offer insight into what to do, and what not to do, when it comes to using SoR in the classroom for strategic reading instruction.
We can summarize many of the points to say that differentiated instruction is key to the success of early readers. SoR is amazingly effective, but not if everyone practices the same things at the same pace with the same intensity.
Also, the need for high-quality instructional materials and resources that drive engagement is highly beneficial. Books need to be appropriate for different skill levels, and the learning environment should be stimulating enough to sustain learning motivation.
All the various components of SoR have to be taught, but in accordance with what each student needs. Differentiation can take up time and extra resources, which are common challenges. But, differentiated instruction has a host of advantages which can offset these challenges and ultimately ensure that every kid has their best foot forward in reading.
Any tool that makes it easy to differentiate lessons and monitor individual students in a cost-effective manner, will save teachers percioustime. And if those tools also include guidance on SoR-based teaching practices, plan lessons for their students, and review any progress made, those time savings become truly significant.. That newly freed time can be used to help struggling readers who require further support.
Applying These Lessons

That wraps up this article on the 40 SoR insights. Sprig hopes that the guidance offered here is used to strategize reading instruction in line with SoR.
Want help bringing SoR into your classroom? Get in touch with us.
Educators are the heartbeat of the education system. They have a lot on their plate. At this time when there is increasing consensus around SoR, it’s important to be strategic about how reading instruction is delivered across schools and districts.
Sprig Learning is developing Sprig Reading, which will be released in the fall and change the face of SoR-based early literacy instruction.
Having the right plan to begin with will save teachers time, and ensure students have enough support.






















